Week 9 11
Application-level and advanced high-level topics in Machine Learning
Anomaly Detection System
Gaussian Distribution
Anomaly detection uses gaussian distribution - probability density function formula

The hypothesis model uses density estimation, the product of all density functions , to detect frauds

The concept here is deeply incorporated into another concept likelihood - the anonymous data points usually have low likelihood
Likewise, anonymous data points usually have low value in density estimation function
Feature engineering
Instead of , one can do log transform or change the degree of feature to form gaussian-like shape to make model happy e.g.
, or
Sometimes is not that comparable (say, both large) for normal and anonymous data.
- To solve this problem, we can define new features e.g. which can help capture unusually large or small values (outliers)
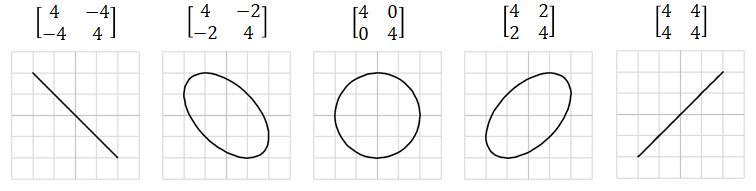
Multivariate Gaussian Distribution
Motivation: what if normal data points cluster don't follow standard gaussian distribution shape - normal data are not within perfect circle but oval instead even when features are normalized (when feature engineering can't help a lot).
e.g. normal (red) vs. anonymous (green) - we can't draw circle (pink) bound to separate two classifications but need to draw oval (blue) bound below

Model hypothesis:



Similar to normal gaussian distribution step, to detect anonymous data using multivariate gaussian distribution, we plug data into model and use a threshold

Multivariate vs. single variate
So multivariate gaussian model basically is a more general form with flexible covariance matrix , where original normal gaussian model requires to be diagonal

Large Scale Machine Learning
Different names for different kind of gradient descents
batch/mini-batch/stochastic gradient descent
Online Learning
In computer science, online machine learning is a method of machine learning in which data becomes available in a sequential order and is used to update the best predictor for future data at each step, as opposed to batch learning techniques which generate the best predictor by learning on the entire training data set at once.
Photo OCR
